How to Calculate the Force Required for a Gas Strut
If you wish to fix gas struts to a new application then please see our free design service. We can specify the correct gas struts, mounting locations and brackets for your application. As well as helping you to order a strut, we can also re-gas your old struts. Take a look at our supply of adjustable gas struts - they allow you to vent gas from the strut (lowering its force) once it has been mounted, until the exact force required is achieved. This is often a better option than using fixed force gas struts for a one-off application.
Gas Springs Lift Calculator
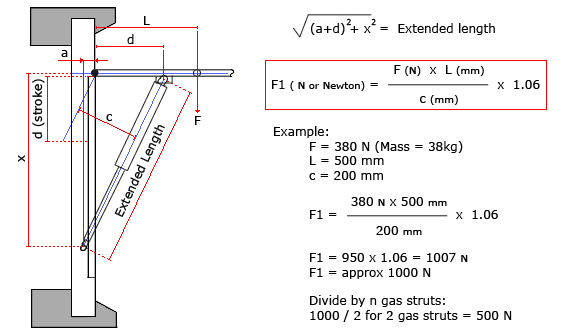
There are a large number of applications for gas struts. Whether you would like to add some spring to your Ottoman bed, fix a roof light, campervan bonnet or roof box, a different calculation will be required for each new gas strut application. Configure your gas strut yourself with our gas spring force calculator. Gas Strut Force Calculation A gas strut calculator will take into account the direction of operation for the particular application, the operating arm, the weight and force relation. Use our gas strut force calculation formula below to work out the force needed. (d) distance from the hinge is recommended at approximately 20% of the panel length. (F) weight is the mass in Kg multiplied by 10. Help Centre Here at SGS, we have a large stock of gas struts and gas springs that have been manufactured in our new modern purpose built facility in Derby. Perfect for both domestic and commercial applications, you can find exactly what you’re looking for with our huge collection of gas struts and industrial gas springs. Even if you can’t find your industrial gas strut online, our sales team can still help – contact us today for a same-day quote.
 Help Centre Here at SGS, we have a large stock of gas struts and gas springs that have been manufactured in our new modern purpose built facility in Derby. Perfect for both domestic and commercial applications, you can find exactly what you’re looking for with our huge collection of gas struts and industrial gas springs. Even if you can’t find your industrial gas strut online, our sales team can still help – contact us today for a same-day quote.
Help Centre Here at SGS, we have a large stock of gas struts and gas springs that have been manufactured in our new modern purpose built facility in Derby. Perfect for both domestic and commercial applications, you can find exactly what you’re looking for with our huge collection of gas struts and industrial gas springs. Even if you can’t find your industrial gas strut online, our sales team can still help – contact us today for a same-day quote.